“GROWTH AND PERFORMANCE OF MICRO, SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTERPRISES IN INDIA”
1. INTRODUCTION TO MSME:
MSME acronym to Micro, small and medium enterprises, in accordance with Micro, small & medium enterprises development act, 2006 classified into two classes:
Ø Manufacturing enterprises, which involved in the manufacture or production of goods relating to any industry specified in schedule of Industry act 1951 or employing plant and machinery in the process of value addition to final product having a discrete name or character or use and defined in terms of investment in plant & machinery:
Ø Micro enterprise– does not exceeds 25 lakh rupees,
Ø Small enterprise–more than 25 lakh but less than 5 crore rupees,
Ø Medium enterprise– more than 5 crore but less than 10 crore rupees.
Ø Service sector, which engaged in providing or rendering services and defined in terms of investment in equipment:
Micro enterprise- does not exceeds 10 lakh rupees,
Small enterprise –more than 10 lakh but less than 2 crore rupees,
Medium enterprise – more than 2 crore but less than 5 crore rupees.
2. OVERVIEW OF INDIAN MSME:
Over last 5 decades MSME sector emerged as ex
tremely effervescent and vigorous segment of Indian economy. MSME plays dual role of providing employment and industrialization of rural/backward areas, thereby reducing regional imbalance and equitable distribution of national income. MSME’s are harmonizing to large industries as supplementary units, which adds to socio economic development. It consists of 36 million units, providing employment over 80 million persons with 8% contribution to GDP.
tremely effervescent and vigorous segment of Indian economy. MSME plays dual role of providing employment and industrialization of rural/backward areas, thereby reducing regional imbalance and equitable distribution of national income. MSME’s are harmonizing to large industries as supplementary units, which adds to socio economic development. It consists of 36 million units, providing employment over 80 million persons with 8% contribution to GDP.
Leading industries of MSME sector (as per 2014-15 MSME report):
Ø Retail trade( except of motor vehicle & motor cycles) and Repairs of personal and household goods – 39.85%
Ø Manufacturing of wearing apparels- 8.75%
Ø Manufacturers of foods and beverages-6.94%
Ø Other services activities -6.2%, other business activities – 3.77%
Ø Hotels and restuarents-3.64%
Ø Sales maintenance of motor vehicles and cycles – 3.57%
Ø Furniture manufacturing -3.21%, Textile -2.33%
Ø Fabricated metals except machinery and equipment-2.33% and others 19.4%. According to India MSME report 2014, three sub sectors demonstrates promising picture: food processing- high potential because of agro linkage, textiles-innovation, and electronics- linkage with ITES.
3. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY:
Ø To understand the various problems faced by MSME
Ø To analyze the performance of MSME: employment and investments
Ø To analyze the contribution of manufacturing output of MSME in GDP
MSME contributes immensely to Indian economy through creating employment, production, innovation and development and enriching entrepreneurship skills. However, MSME’s faces many problems, which includes: unduly delayed payments by large industry players, absence of timely credit, lack of infrastructure input, limited capital & knowledge, low managerial capability, low ROI, low production & productivity, inefficient marketing strategies, non-identification of new markets, hurdle in expansion & innovation, lack of warehousing, ruthless competition and decline exports of total exports.
5. DATA ANALYSIS:
Table 5.1: Performance of MSME, Employment and Investments
Sl No. | Year | Total working enterprise (in lakh) | Employment (in lakh) | Market value of fixed Asset (Rs. In crore) |
1 | 2006-07 | 361.71 | 805.23 | 868,543.79 |
2 | 2007-08 | 377.36 | 842.00 | 920,459.84 |
3 | 2008-09 | 393.7 | 880.84 | 977,114.72 |
4 | 2009-10 | 410.8 | 921.79 | 1,038,546.08 |
5 | 2010-11 | 428.73 | 965.15 | 1,105,934.09 |
6 | 2011-12 | 447.64 | 1011.69 | 1,182,757.64 |
7 | 2012-13 | 447.54 | 1061.4 | 1,268,763.67 |
8 | 2013-14 | 488.46 | 1114.29 | 1,363,700.54 |
Sources: Annual report 2014-15, GOI, Ministry of MSME
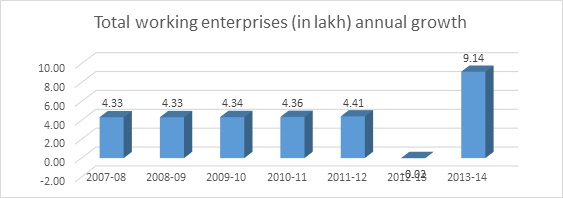
Chart 5.1: chart showing annual growth rate of total working enterprises in MSME
Sources: author’s calculation
Chart 5.2: chart showing annual growth rate of employment in MSME
Sources: author’s calculation
Chart 5.3 chart showing annual growth rate of Market value of fixed assets in MSME
Sources: author’s calculation
Analysis: Total working enterprise in MSME grown at CAGR 4.39% from 2006-07 to 2013-14, there is fluctuation in annual growth rate and during 2012-13 negative growth in total working enterprises. Employment growth in CAGR 4.75% from 2006-07 to 2013-14, there is continuous growth in MSME employment and MSME providing more employment opportunities over last 7 years. Market value of fixed asset growth in CAGR stands at 6.65% from 2006-07 to 2013-14, market value increased over a period of time.
Table 5.2: Contribution of manufacturing output of MSME in GDP
Sl No | Year | Gross Value of Output of MSME Manufacturing Sector ( in crore) | Share of MSME sector in total GDP (%) | Share of MSME Manufacturing output in total Manufacturing Output (%) | ||
Manufacturing Sector MSME | Services Sector MSME | Total | ||||
1 | 2006-07 | 1198818 | 7.73 | 27.40 | 35.13 | 42.02 |
2 | 2007-08 | 1322777 | 7.81 | 27.60 | 35.41 | 41.98 |
3 | 2008-09 | 1375589 | 7.52 | 28.60 | 36.12 | 40.79 |
4 | 2009-10 | 1488352 | 7.45 | 28.60 | 36.05 | 39.63 |
5 | 2010-11 | 1653622 | 7.39 | 29.30 | 36.69 | 38.5 |
6 | 2011-12 | 1788584 | 7.27 | 30.70 | 37.97 | 37.47 |
7 | 2012-13 | 1809976 | 7.04 | 30.50 | 37.54 | 37.33 |
Sources: Annual report 2014-15, GOI, Ministry of MSME
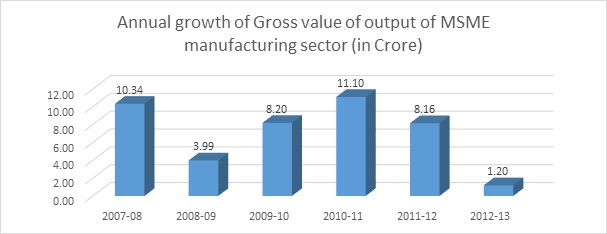
Chart 5.4: chart showing annual growth rate of gross value of output of MSME manufacturing sector
Sources: author’s calculation
Chart 5.5: chart showing share of manufacturing, services and total MSME growth to GDP
Sources: author’s calculation
Analysis: Gross value of output of MSME manufacturing sector (in crore) grown at
CAGR of 7.17% during 2006-07 to 2012-13 and the growth rate highly fluctuated. Share of manufacturing sector growth rate to GDP with CAGR of negative -1.53% during 2006-07 to 2012-13 and indicates MSME manufacturing industry contribution to GDP is down over 6 years of period. Share of service sector growth rate to GDP with CAGR of 1.82% during 2006-07 to 2012-13 and indicates MSME service industry contribution to GDP is growing lower over 6 years of period.
6. GOVERNMENT POLICY INITIATIVES:
Ø Implementation of MSME development act 2006, which provides rules and regulation for MSME
Ø Reservation and de reservation of products for manufacture in MSME sector- to achieve socio economic development, enhancing technological and achieving economies of scale.
Ø National manufacturing competitiveness program – to build sustainable capacity, overcoming global competitiveness and healthy growth through eight components which includes: incubator, intellectual property awareness, quality management, technology up gradation, marketing assistance, design expertise and promotion of ICT.
Ø Public procurement policy through implementation of technology in tenders.
Ø E-governance – to facilitate employment, virtual cluster, share database, B2B portal and mobile friendly website.
7. CONCLUSION:
Though MSME total working enterprises, employment and market value of fixed assets grown at CAGR of 4.39%, 4.75% and 6.64% respectively, the contribution from manufacturing and service sector MSME contribution to GDP is -1.53% and 1.82% respectively. Though government has taken measure to improve the productivity, over last 7 years the MSME contribution to GDP has not increased to acceptable level. It is suggested that government has to adopt integrated policy, providing sound data with efficient governance, promote skill development to increase productivity and providing accessible credit through government sponsored agency exclusively to MSME is essential to increase productivity and contribution to economic growth.
8. REFERENCES:
<Annual report, 2014-2015, Government of India, Ministry of MSME>
<Dr. M S Vasu, Growth and Development of MSME in India: Prospects and Problems, India Journal of Applied research, Vol-4, Issue-5, May 2014>
< Entrepreneurs memorandum (part-ii) data on MSME sector, development commissioner, ministry of MSME>